
Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) Anaerobic Digestion Energy Basics. Further general information is available through the U.S. This overview is intended to provide specific details for Federal agencies considering biogas technology as part of a major construction project. As of December 2010, there are 541 operational landfill gas energy projects in the United States and approximately 510 landfills that are good candidates for projects. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Landfill Methane Outreach Program estimates that a landfill gas energy project will capture roughly 60% to 90% of the methane emitted from the landfill, depending on system design and effectiveness. Methane is a very potent greenhouse gas-more than 21 times stronger than carbon dioxide-and is a key contributor to global climate change. However, projects located near a landfill or contained animal feeding operation may want to consider this option since it can provide low-cost energy. Biogas is not a widely used renewable energy technology for most new construction or major renovation projects since most buildings do not have a large source of organic material.
Sewage sludge and animal slurries usually end up as fertilizer, so it is better to obtain fuel from them first, while preventing runoff and methane emissions at the same time.

When biogas is created from existing waste streams, it reduces odors and methane emissions and creates two renewable resources. Methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide can be combusted to create heat and electricity. Other common gases that can be formed include hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide. The most common gases produced are methane and carbon dioxide.
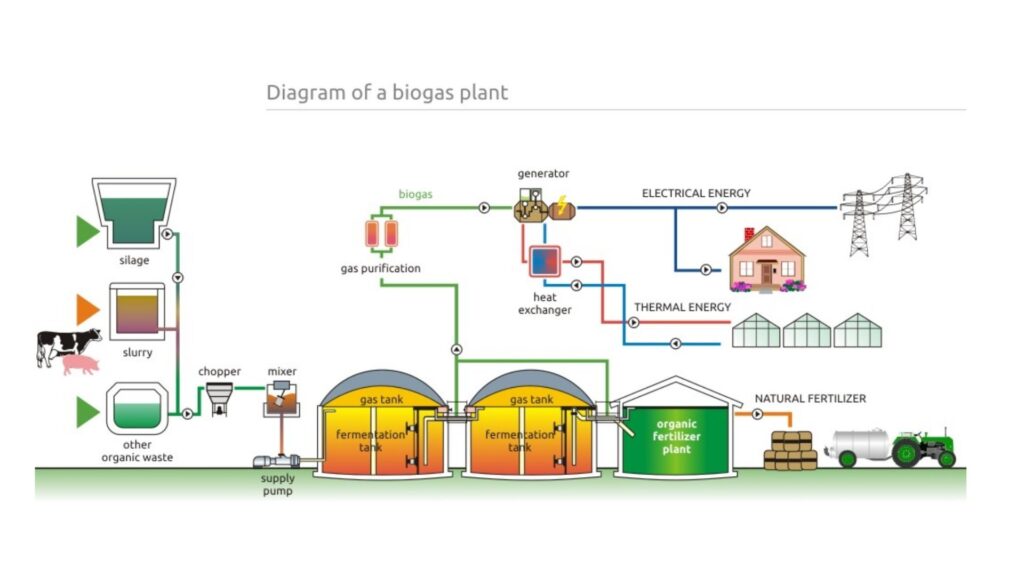
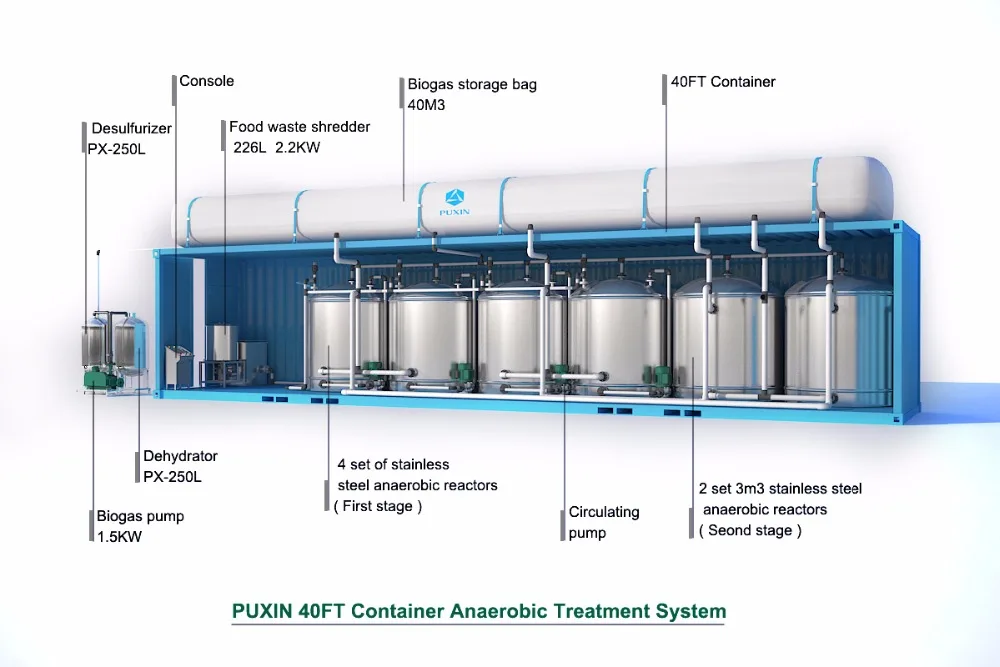
The types of organic materials include biomass, landfill waste, sewage, manure, and plant material. An anaerobic digestion plant was built to process sewage in Bombay in 1859, and has been used in the United Kingdom since 1895. Anaerobic digestion is a process that uses microorganisms to break down the organic material in the absence of oxygen, which creates energy. The organic materials are then oxidized and create energy, which dates back to ancient Persians who observed that rotting vegetables produce flammable gas. Fermentation, or anaerobic digestion, is the most common process that breaks down the organic materials. Biogas is the gas produced by the biological breakdown of organic materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
